Technical Resources
Download & study documents on the EPIC system
Documents
International Erosion Control Association paper discussing a paradigm shift in stormwater management.
Discussion of aggregate filters applied to roads, parking lots, alleys, and hardscapes. The EPIC system acts as a passive oil and grease separator, along with bio-treatment of various other contaminants, through the natural processes of biology and nature.
Part 2 of the SR 28 articles shows road filter performance results in Lake Tahoe.
Evaluate the inventor’s details, background, and philosophy that created the Environmental Passive Integrated Conveyance apparatus and method. Patented Proprietary Information for Regulators and Installers of Individual Home Sewage Systems.
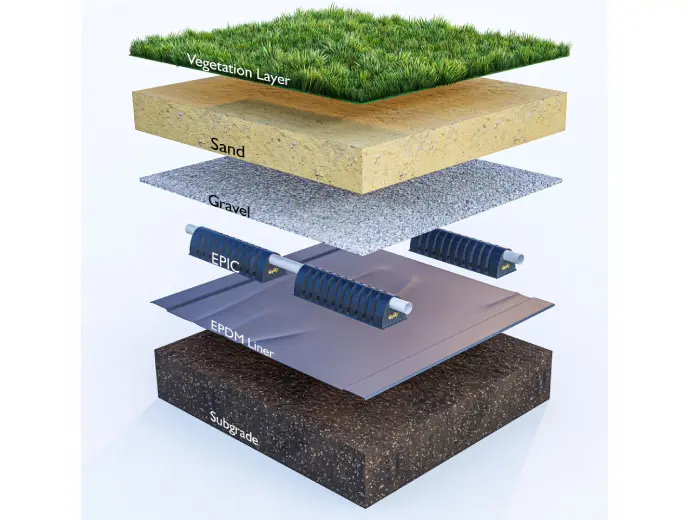
Synthetic Turf Cooling EPIC Base
Heat trial case study performed in Phoenix, AZ, testing EPIC system sand base as a cooling mechanism through capillary physics to extend playable time on synthetic turf surfaces. Results that are over 50 degrees (F) cooler than conventional methods.
A technical report from New Mexico State University comparing USGA golf greens. The study included sprinklers, subsurface drip, and subsurface ECS (EPIC System) sand hydroponic technologies. ECS golf greens in the study used 70% LESS WATER than sprinklers/drip and yielded BETTER TURF QUALITY!
A white paper discussing water use and transpiration. In 2001, a study was conducted to measure the water use of 4 acres of turf in EPIC fields in the high desert of Reno, NV. The supplemental water was metered and evapo-transpiration (ET) rates in the EPIC system are amortized over the course of a year to average 0.15 gallons per square foot per day.
Wildwood Commons - Nutrient Reduction in runoff
Description of pollutant removal, including an 85% reduction of phosphates utilizing the EPIC system at a monitored residential housing project.
Final Project Monitoring Report-Westside Park
The City of Los Angeles project monitoring report for Westpark includes results of Ecoli bacteria reduction by 97% by subsurface sand filters.
A comparison of turf maintenance between clay, loam, sand, and EPIC fields. Technical analysis of turf maintenance, including mowing, aeration, nutrient balance, and identification of various diseases.
A photographic tour of EPIC system technology and applications in the USA and Middle East. Various installation pictures and schematics allow you to visually browse through 25 years of EPIC history. Fields, Parks, Agriculture, Net Zero Projects, Grey Water Reuse, and Salt Water Irrigation R&D
Water Facts and Equations
Regional Representatives
Certified Contractors
Contact us for business opportunities
EPIC System Components Partners
Spec Sheets
ACAD Details
DWG files are available upon request.

